
Artificial Snow May Buy Time for Ski Resorts but Cannot Outrun Climate Change
As the 2026 Milan Olympics lean on snow machines, researchers warn that snowmaking locks resorts into a costly path with an expiration date.
via phys.org
Scientific discoveries and research

As the 2026 Milan Olympics lean on snow machines, researchers warn that snowmaking locks resorts into a costly path with an expiration date.
via phys.org

A University at Buffalo study finds the chin likely arose as a byproduct of skull changes, not through natural selection for a specific function.
via phys.org

Mineral analyses near Pavonis Mons show Martian volcanoes evolved through multiple eruption phases, not single events as long assumed.
via phys.org

A carbon-nanotube-based abrasive achieves over one billion grit, smoothing semiconductor surfaces to within a few atoms while eliminating toxic slurry.
via sciencedaily.com

Deep learning models and expanded NOAA mapping now cover 60 percent of the U.S. population, promising faster, more accurate flood forecasts.
via sciencedaily.com

Researchers confirm that the thousands of microtubules in cell-division spindles self-organize according to active liquid crystal physics.
via phys.org
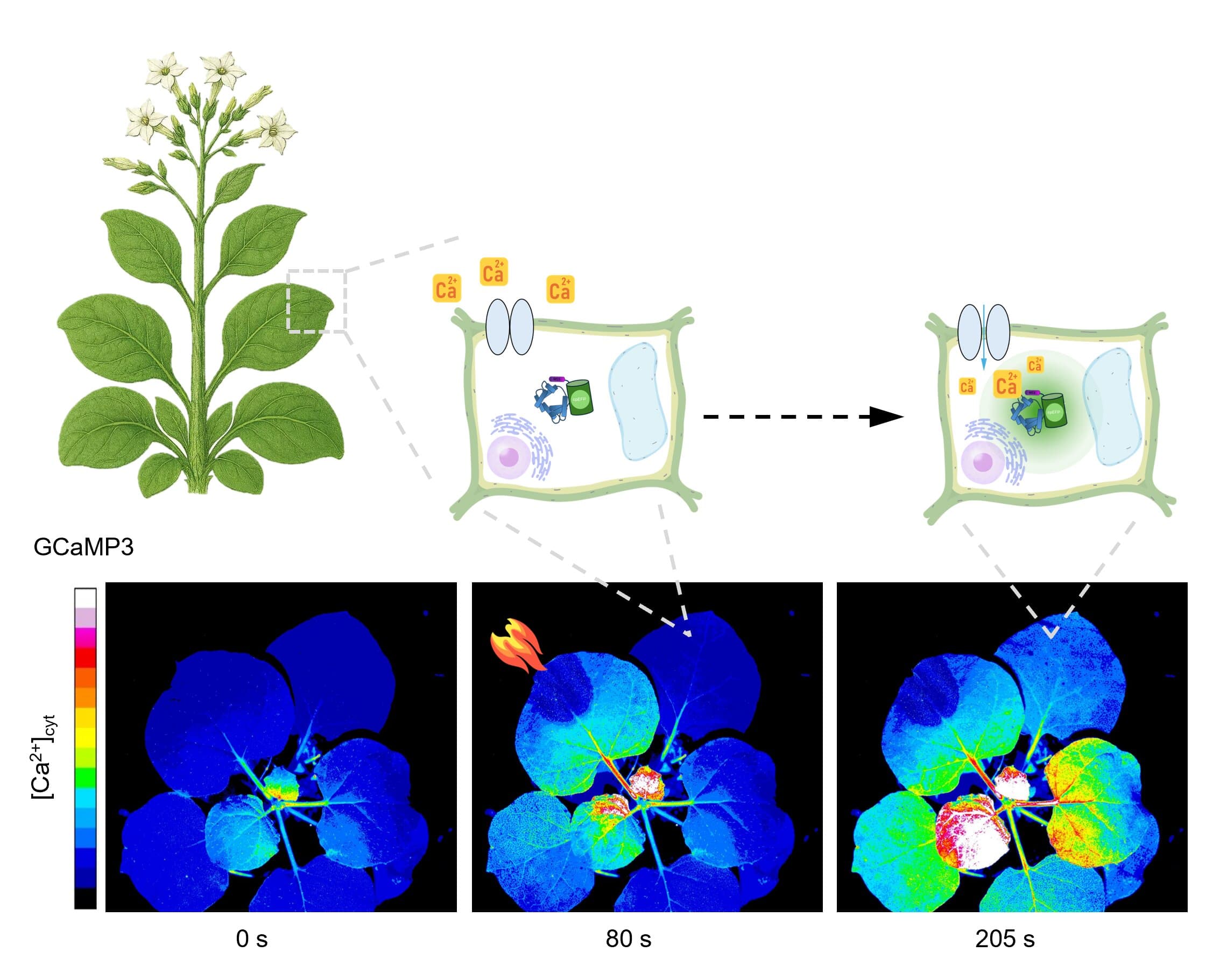
An open-source optical system captures calcium and glutamate signals traveling bidirectionally through entire adult plants under environmental stress.
via phys.org

University of Amsterdam researchers reveal how subtle ion shifts in viscous salt solutions trigger nanocrystals to self-assemble into sea-urchin-like spherulites.
via sciencedaily.com

As climate change shrinks natural snowfall, ski resorts face a paradox. Artificial snowmaking sustains the industry but carries huge environmental costs.
via sciencedaily.com

A new study reveals the human chin is not an adaptation but a byproduct of evolutionary changes to our face, solving a century-old anthropological mystery.
via sciencedaily.com
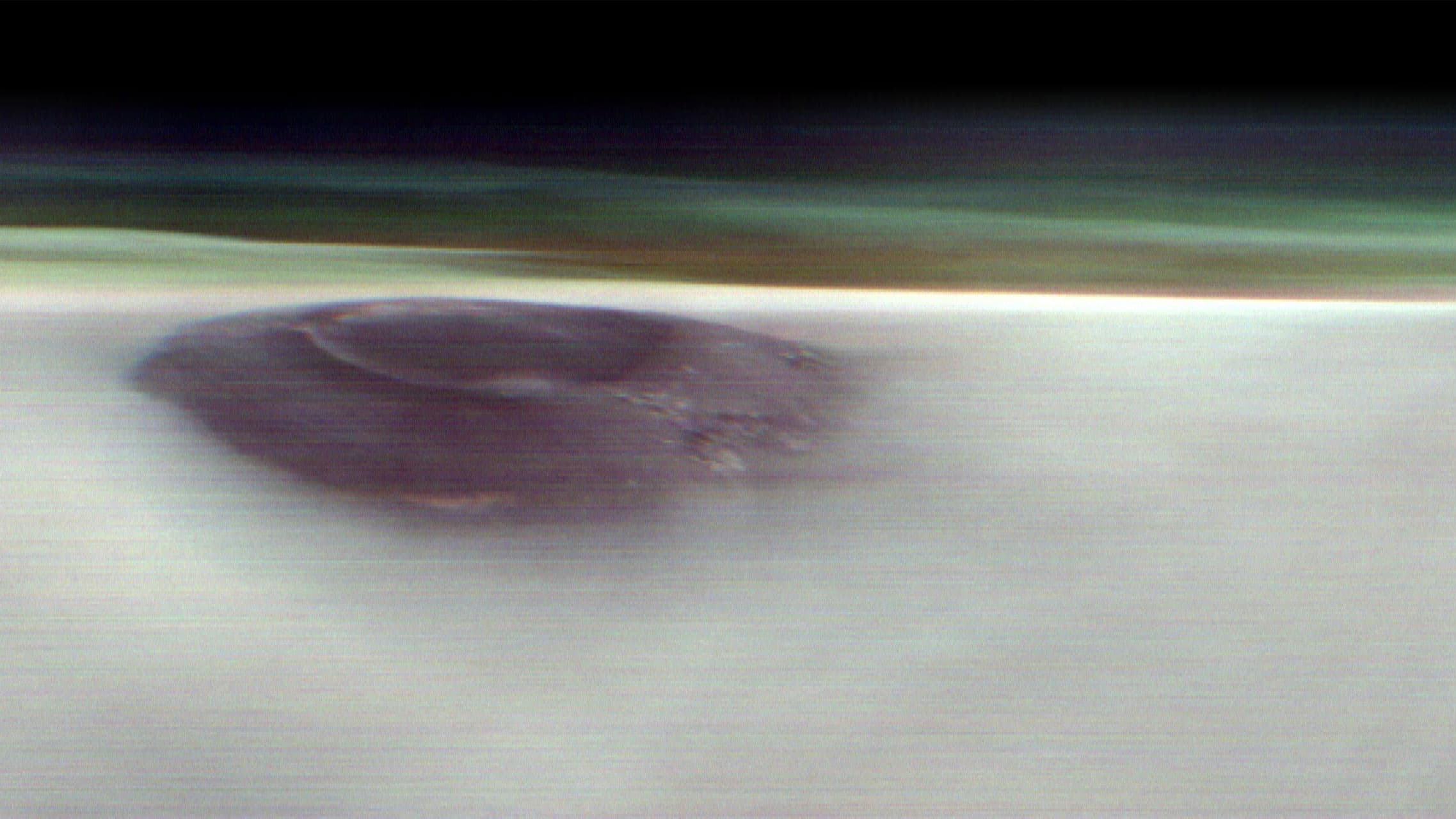
New analysis of young Martian volcanoes reveals surprising diversity in eruption styles and compositions. It challenges assumptions about Mars geology.
via sciencedaily.com

Engineers developed a carbon nanotube polishing method achieving atomic-level flatness on semiconductor surfaces. It is a next-gen chip breakthrough.
via sciencedaily.com

A new AI-powered flood prediction framework outperforms traditional models. It delivers faster, more accurate forecasts across entire river networks.
via sciencedaily.com
A new theoretical framework proves that spindles driving cell division behave like liquid crystals. The finding reshapes cellular self-organization.
via sciencedaily.com

A new imaging breakthrough reveals how plants send distress signals between leaves, stems, and roots in real time. It rewrites plant biology.
via sciencedaily.com

Researchers decoded the mechanism behind how nanocrystals self-assemble into perfect spheres. The breakthrough opens new doors for advanced materials.
via sciencedaily.com

In what environmental groups are calling one of the most consequential regulatory rollbacks in modern American history, the Environmental Protection Agency has moved to formally revoke its 2009 endang
via arstechnica.com